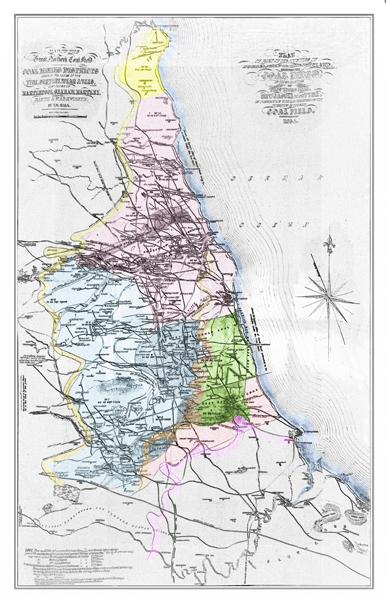
Uncovering the Historical Significance of England’s Great Northern coalfield
The Great Northern Coalfield represents more than just a sprawling expanse of collieries and mining towns; it is a testament to the exceptional industrial evolution that shaped modern England. At its peak during the 19th and early 20th centuries, this region became a powerhouse of productivity, propelling both local and national economies. The coal extracted here fueled the factories of the Industrial Revolution and powered the homes and industries that defined a generation. Significant towns such as Newcastle, Durham, and Sunderland emerged as key players in the global coal market, with intricate networks of railways that facilitated the transportation of coal, transforming the socio-economic landscape of northern England. The legacy of this resource is evident in the architecture, culture, and communities that evolved around it, marking a pivotal chapter in the narrative of British industrialization.
While the coalfield’s peak production has long as passed, its historical significance cannot be understated. It is indeed not merely a geographical area but a living history that highlights the ingenuity and resilience of its workers. As we uncover the stories of miners, their families, and the communities built around coal mining, we gain insight into the struggles and triumphs that shaped their identity.Key events, such as the miners’ strikes of the 20th century, serve as reminders of the ongoing fight for workers’ rights and social justice. Furthermore, the transition from a coal-centric economy to a diversified one showcases the adaptability of the region, paving the way for a contemporary narrative that blends respect for its industrial past with a vision for a sustainable future.
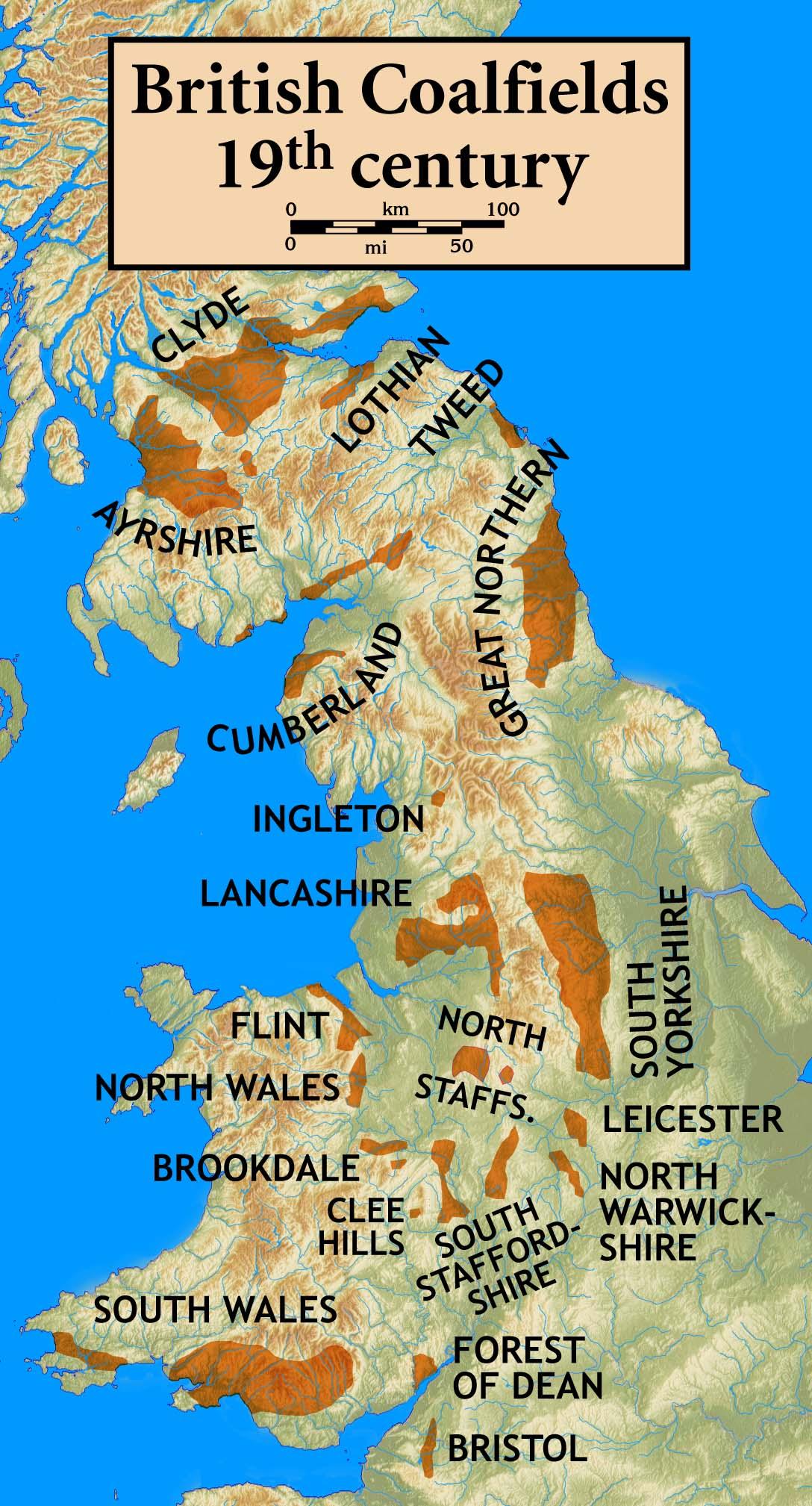
Exploring the Environmental Legacy and Challenges of Coal Mining
The legacy of coal mining in England’s Great Northern coalfield is a tapestry woven with both industrial triumphs and ample environmental repercussions. Once the backbone of Britain’s industrial prowess, the region’s rich deposits fueled factories, railways, and homes, driving economic expansion during the industrial revolution. Though, the cost of this progress has emerged, revealing alarming challenges, including:
- Soil Degradation: Extensive mining operations have led to significant soil erosion, impacting agricultural productivity in surrounding areas.
- Water Pollution: Acid mine drainage has contaminated local waterways,posing risks to aquatic life and drinking water quality for nearby communities.
- Air Quality Issues: Emissions from coal dust and mining activities have contributed to health concerns, particularly respiratory ailments among populations living near former mining sites.
As the remnants of mining in the Great Northern Coalfield stand as a stark reminder of its dual legacy, the challenge of reclamation looms large. Restoration initiatives aim to rehabilitate devastated landscapes and revitalize ecosystems. Yet,these efforts are often hindered by lingering pollution and land instability left in the wake of extensive extraction. Addressing these environmental scars requires a multifaceted approach, merging community engagement with innovative technologies to diminish the long-lasting impacts of coal mining, while also fostering a sustainable future for the region. The ongoing reconciliation of industrial history with environmental stewardship poses a critical test of society’s commitment to living harmoniously with the land.

Revitalization Efforts in Former Mining Communities
As the remnants of the Great northern Coalfield stand as both a historical landmark and a canvas for regeneration, numerous initiatives are breathing life back into former mining communities. Local governments and grassroots organizations are collaborating to transform abandoned sites into vibrant spaces that foster community spirit and economic growth. Through strategic investments and creative planning, these areas are witnessing a renaissance that emphasizes the preservation of cultural identity while adapting to modern needs.Key efforts include:
- Creation of green spaces: Former mining sites are being converted into parks and recreational areas, promoting environmental sustainability and community well-being.
- Support for local businesses: Initiatives aimed at downtown revitalization are providing essential resources and funding for small enterprises, encouraging job creation and economic stability.
- Historical preservation projects: efforts to maintain and showcase the rich mining heritage are ongoing,ensuring that the stories of past communities are honored and integrated into the revitalized landscape.
The conversion of these communities extends beyond physical changes; it aims to rebuild a sense of identity and belonging among residents. Engagement with local voices is crucial in this process, as community members are invited to contribute ideas and solutions that resonate with their experiences. Educational programs and workshops are playing a pivotal role in empowering residents, equipping them with skills necessary for future opportunities. As a result, the narrative surrounding these areas is shifting from one of decline to one of innovation and resilience, capturing a new chapter in their unfolding story. Initiatives highlighted include:
- Community-led events: Festivals and markets are being developed to celebrate local culture and to boost social cohesion.
- skills training and apprenticeship programs: Collaborations with local colleges and businesses are offering hands-on experience and education, preparing the workforce for emerging industries.
- Public art installations: Artists are commissioned to create murals and sculptures that reflect the local heritage and aspirations,fostering a sense of pride and belonging.
Future prospects: Transitioning from Coal to Sustainable Energy Solutions
the transition from coal to sustainable energy solutions is not merely a matter of choice; it is an urgent necessity driven by environmental imperatives and technological advancements. As the Great Northern Coalfield bids farewell to its coal mining legacy, the focus is now shifting towards a range of renewable energy sources that promise a cleaner, more sustainable future. Key areas of investment and development include:
- Solar Power: Harnessing sunlight through photovoltaic cells, solar energy is rapidly becoming a frontrunner in the race towards renewables, with potential for extensive deployment across former mining sites.
- wind Energy: both onshore and offshore wind farms are gaining traction, transforming the landscapes of northern England into hubs of clean energy generation.
- Hydroelectric Systems: Utilizing the region’s rivers and waterways, small-scale hydro installations could contribute significantly to the local energy mix.
- Biomass solutions: Revitalizing waste materials into energy sources offers a dual benefit of reducing waste while providing reliable power.
In parallel with these technological advancements, there is an innovative push towards community engagement and education to ease the transition. local governments and organizations are prioritizing transparency and inclusion,ensuring that affected communities have a voice in shaping their energy future. Training programs are being implemented to prepare workers for new roles in sustainable energy sectors, aiming to build a resilient economy that thrives on renewable sources. Through collaborative efforts, the legacy of coal mining can forge a new path toward sustainability, reflecting not only a change in energy production but also a revitalization of community spirit and environmental stewardship.