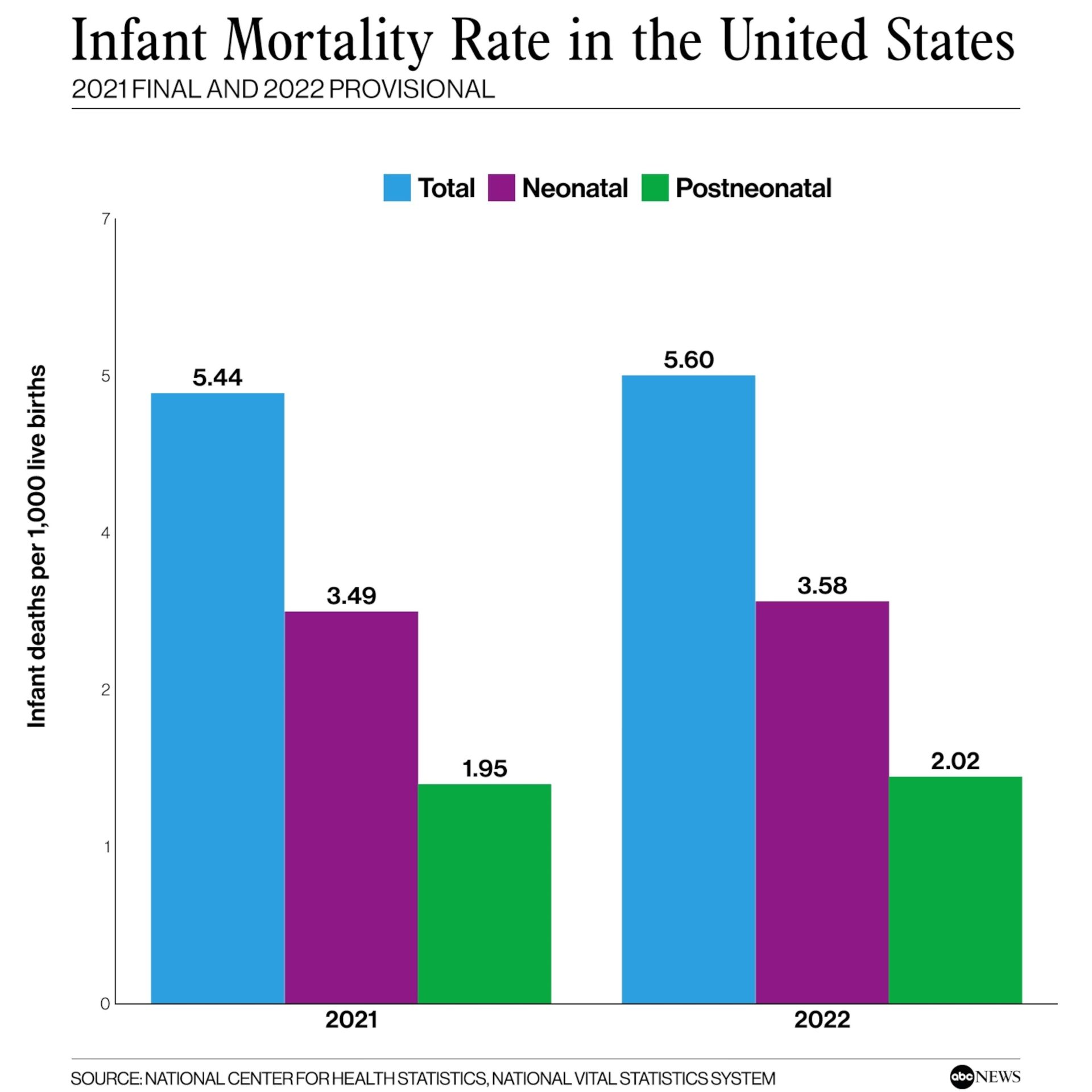
Impact of Abortion Bans on Infant Mortality Rates in the United States
Recent research has illuminated a troubling correlation between abortion bans and rising infant mortality rates in the United States. States that have enacted stringent abortion restrictions tend to experience higher rates of infant deaths, particularly among marginalized populations. This phenomenon can be attributed to several interconnected factors, including decreased access to extensive reproductive healthcare, increased maternal stress, and a higher likelihood of preterm births. as access to safe and legal abortion services diminishes, the healthcare system’s ability to support at-risk pregnancies also dwindles, creating a perfect storm for adverse health outcomes.
Moreover, the ramifications of these bans extend far beyond individual cases, impacting public health at a systemic level. The following factors contribute significantly to the observed increase in infant mortality rates in states with abortion restrictions:
- Economic strain: Many women denied abortions face financial hardships, leading to inadequate prenatal care.
- Healthcare Disparities: Low-income and rural women frequently enough have limited healthcare options,exacerbating health inequities.
- Delayed medical Intervention: Complications that may warrant abortion can escalate when such options are unavailable.
These elements create a dire public health crisis, raising urgent questions about the implications of reproductive rights on maternal and infant health outcomes across the nation.
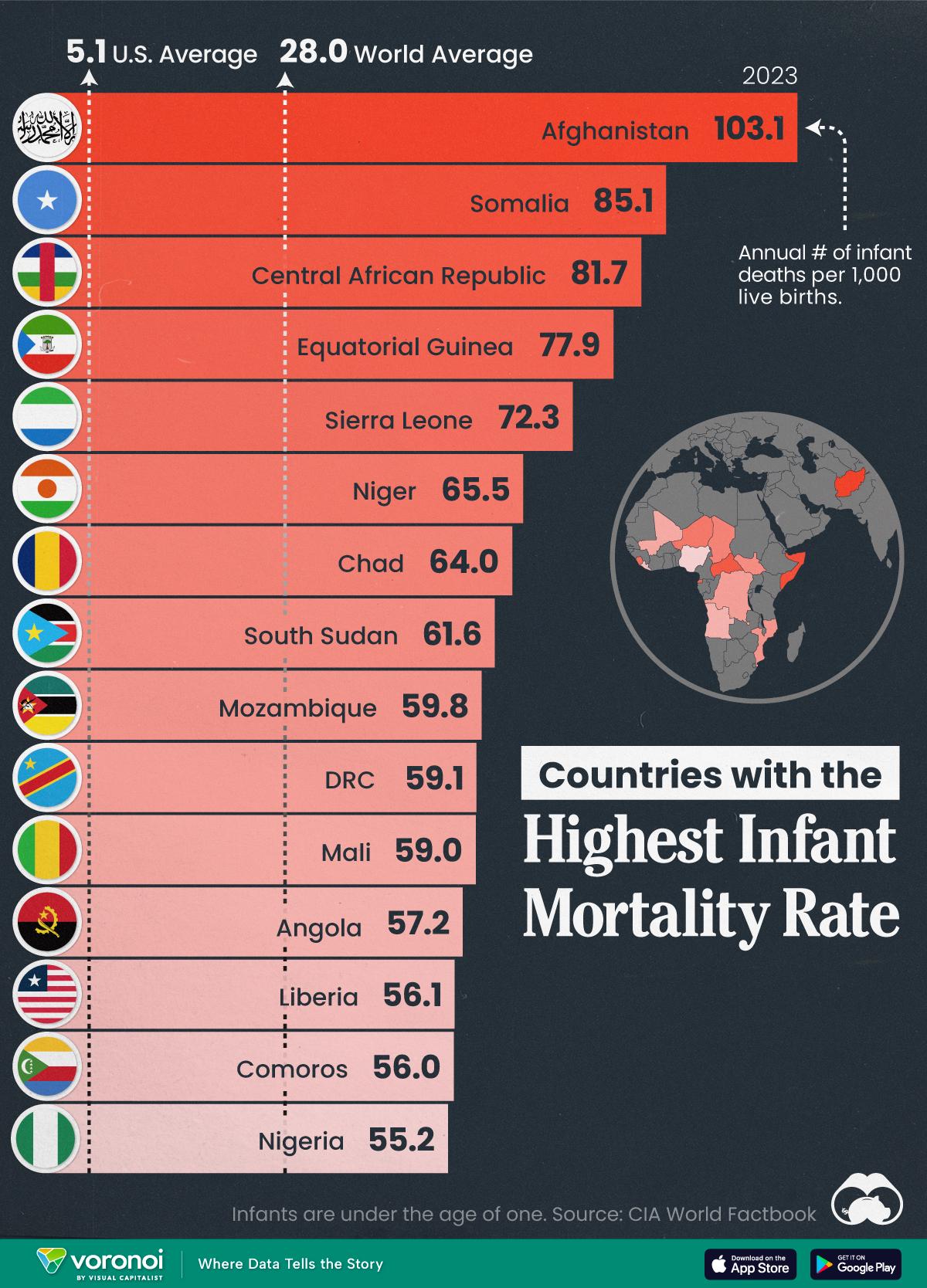
Analysis of Socioeconomic Factors Contributing to Increased Risks
The findings of the study underscore a complex web of socioeconomic factors that exacerbate the risks associated with rising infant mortality rates in states where abortion bans are enforced. Limited access to healthcare services is a primary concern; these states often face shortages of maternal and child health resources. This lack of access can lead to inadequate prenatal care,which is essential for monitoring potential complications during pregnancy. Additionally, socioeconomic disparities play a significant role, as families in lower-income brackets are less able to afford quality healthcare, nutrition, and other necessary supports that promote healthy pregnancies and births. Communities with higher poverty rates frequently struggle with higher rates of stress and mental health issues, both of which can adversely impact maternal health.
In conjunction with healthcare access issues, educational resources about family planning and reproductive health are often lacking in states with stringent abortion laws. This leads to unintended pregnancies, particularly among vulnerable populations who may lack the knowledge or resources to make informed choices about thier reproductive health. Moreover, these areas frequently enough experience higher rates of systemic inequity, including racial and ethnic disparities, which contribute to an surroundings where infant mortality rates can soar. Economic instability, characterized by unemployment and underemployment, further compounds these challenges, making it harder for families to provide a safe and nurturing environment for their newborns, and ultimately resulting in more tragic outcomes in infant health.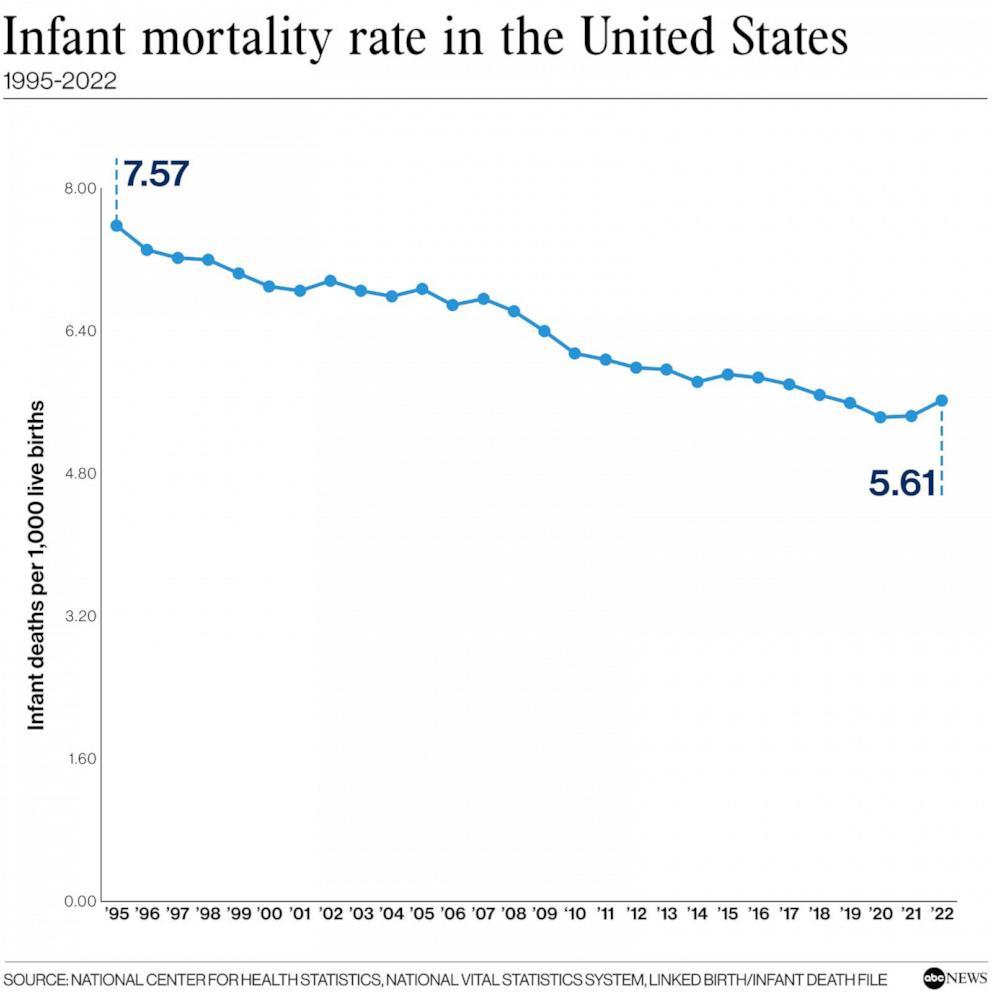
Healthcare Gaps: The Role of Maternal Support Services
The link between maternal support services and infant mortality is becoming increasingly vital as recent studies reveal alarming trends in states with abortion bans. these legal restrictions often exacerbate existing healthcare gaps, leaving vulnerable populations without adequate access to essential services.Maternal support services, which can include comprehensive prenatal care, mental health screenings, and lactation consulting, play a crucial role in mitigating these disparities. When pregnant individuals are provided with consistent support, they are more likely to experience better health outcomes both during pregnancy and after childbirth. This highlights the urgent need for investment in maternal health programs, especially in regions most affected by restrictive abortion policies.
Moreover, the absence of robust maternal support systems can lead to a cycle of disadvantage, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. Factors such as socioeconomic status, education quality, and accessibility to healthcare resources are frequently enough intertwined, contributing to higher rates of infant mortality. To address these gaps effectively, stakeholders must recognize the importance of integrating maternal support services into broader healthcare strategies. Potential solutions include:
- Enhanced access to prenatal and postnatal care: Increasing healthcare provider availability and outreach to underserved areas.
- Community-based support programs: Establishing networks that connect expectant mothers with local resources and peer support.
- Education and advocacy: Providing facts on maternal health rights and available services to empower women in navigating their healthcare options.
By prioritizing and expanding these services, states can work towards closing the gap that exists in maternal and infant health outcomes, ultimately saving lives in the process.
Policy Recommendations for Combating Rising Infant Mortality Rates
Addressing the alarming rise in infant mortality rates,especially in states with stringent abortion bans,requires a multifaceted approach that prioritizes maternal and infant health. Comprehensive healthcare access is essential; states must expand Medicaid coverage to ensure all women, nonetheless of socioeconomic status, can access essential prenatal and postnatal care. additionally, implementing universal healthcare programs could help mitigate the financial barriers that hinder many families from seeking necessary medical services. Enhancing community health initiatives that educate and support expectant mothers can also play a critical role in promoting healthier pregnancies and outcomes.
Moreover, it is indeed crucial to foster a supportive legislative environment that encourages research and innovation in maternal and child health. Policy frameworks should advocate for investment in maternal health programs, particularly in underserved communities, to reduce disparities in infant mortality rates. Strengthening partnerships between healthcare providers, local governments, and non-profit organizations can definitely help facilitate access to resources such as nutritional support, mental health services, and parenting education. Lastly, establishing robust data collection procedures will allow policymakers to identify trends and tailor interventions effectively, ensuring that support is directed where it is most needed.