EU-US Trade Negotiations Stalled Amid Diverging Digital Regulations
The ongoing negotiations between the European Union and the United States have encountered significant roadblocks, primarily due to differing approaches to digital regulations. While both parties aim to foster transatlantic trade and investment, diverging frameworks on issues such as data protection, privacy laws, and digital market access are proving to be major stumbling blocks. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the U.S. approach, which tends to favor a more industry-lead model, have led to complex discussions, with neither side willing to compromise on their core principles. This discord raises concerns about the potential impact on businesses that operate across both markets,as regulatory uncertainty can stifle innovation and hinder economic growth.
Furthermore, the negotiations have highlighted the importance of establishing a harmonized digital ecosystem that acknowledges both regions’ legislative landscapes. Key stakeholders are advocating for greater dialog and cooperation to bridge the gap between these frameworks. Some of the critical issues that need to be addressed include:
- Data transfers: Ensuring secure and efficient data flows between the EU and U.S. without compromising privacy standards.
- Consumer Protection: Aligning regulations that safeguard consumer rights in digital transactions.
- trade Barriers: Reducing non-tariff barriers that arise from conflicting digital regulations.
As the deadlock continues, industry leaders and policymakers are increasingly vocal about the need for a cohesive strategy to navigate the complexities of digital trade, emphasizing that cooperation is essential for fostering a robust transatlantic economic relationship.
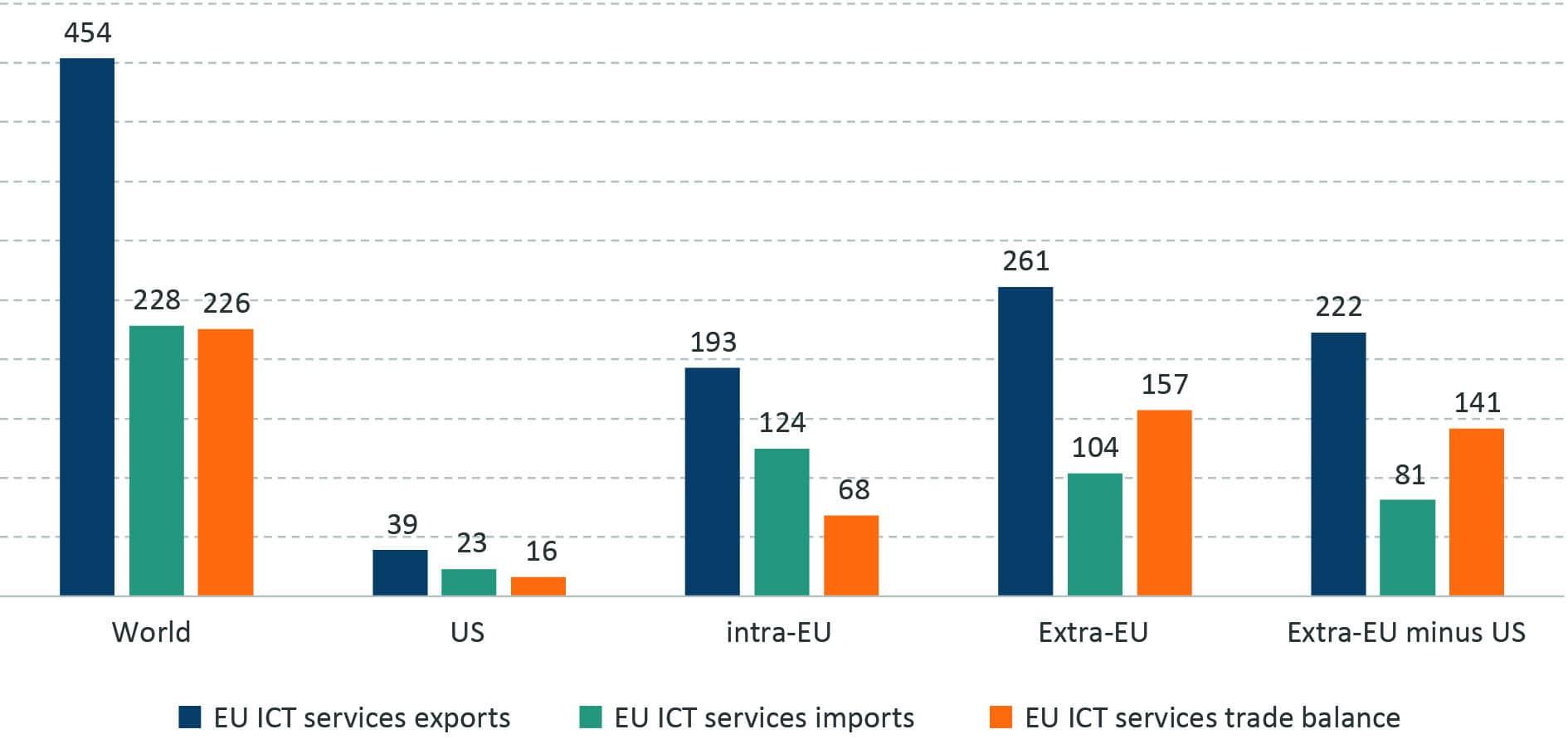
Impact of Eastern European Data privacy Laws on Transatlantic Trade Relations
The increasing stringency of data privacy laws in Eastern Europe is having a profound impact on transatlantic trade relations, particularly between the EU and the United States. As these nations embrace regulations that prioritize the safeguarding of personal data, businesses are confronted with a myriad of compliance challenges. The General Data protection Regulation (GDPR) and variations emerging from Eastern european countries are reshaping how companies handle data across borders,leading to potential friction in trade negotiations. This evolving landscape creates a scenario where American businesses must navigate a complex web of regulations if they wish to maintain access to European markets.
As tensions rise over these digital laws, several key concerns have emerged:
- Compliance Costs: Companies face increased operational costs in adapting to varying regulations.
- Legal Uncertainties: Ambiguities surrounding enforcement and penalties can deter investment and innovation.
- Data Localization Requirements: some Eastern European nations are advocating for data to be stored locally, impacting how U.S. firms operate.
These factors contribute to a cautious atmosphere, as trade talks falter in addressing the nuances of digital governance.As both regions continue to grapple with these challenges,the path toward a cohesive transatlantic digital economy remains uncertain,with repercussions extending beyond commerce into broader diplomatic relations.

Recommendations for harmonizing Digital Standards between the EU and US
To bridge the gap in digital standards between the European Union and the United States, it is essential for both sides to pursue a collaborative approach that acknowledges their respective regulatory frameworks while avoiding duplicative efforts.This can be accomplished through the establishment of joint working groups focusing on key areas such as data privacy,cybersecurity,and digital trade. By integrating insights from both regulatory environments, stakeholders can craft unified guidelines that facilitate smoother transatlantic commerce. Additionally,outreach efforts should be expanded to include industry representatives,policymakers,and civil society to ensure inclusivity and broad acceptance of the digital standards being proposed.
Moreover, laying down a foundation for mutual recognition agreements can significantly streamline the implementation of digital policies.Such agreements would allow for the recognition of each other’s standards without compromising the integrity of either framework. This could extend to areas like cross-border data flows, where joint protocols would mitigate confusion and enhance compliance for businesses operating in both markets. Furthermore, ongoing dialogue and feedback loops should be established to adapt to emerging technologies and regulatory challenges, ensuring that the framework remains relevant and effective over time.

Future Implications of Delayed Trade Agreement on Global Digital Economy
The ongoing delays in finalizing a trade agreement between the European Union and the united states have significant ramifications for the digital economy on a global scale. At the heart of this situation lies a complex web of digital laws and regulations that are diverging between the two economic powerhouses. As technology continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, this impasse can lead to increased uncertainty for businesses reliant on cross-border data flows and digital services. Companies may find themselves navigating a fragmented regulatory environment that complicates their ability to operate efficiently, potentially stifling innovation and hindering investments in crucial digital infrastructure.
Moreover, the potential ripple effects are not confined to the EU and the US alone.Other countries observing the negotiations and the consequent regulatory developments may adjust their own policies, potentially leading to a global misalignment of digital standards. As nations rush to establish their own frameworks, the risk of creating incompatible systems increases, complicating international trade. Key implications may include:
- Increased Costs: Companies may face higher compliance costs as they adapt to varying regulations across borders.
- Slowed Innovation: Businesses may delay or scale back investments in new technologies while awaiting clearer guidelines.
- Market Fragmentation: A lack of uniform standards could lead to a fragmented digital market, hindering cross-border trade.